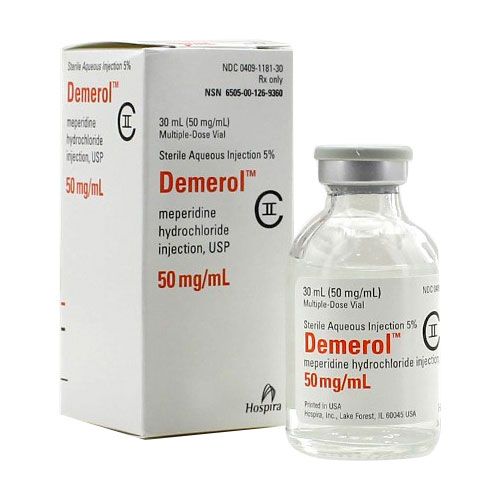
Demerol 50mg/ml 30ml ampul
$100.00
Specifications
Brand Name: Demerol, Pethidine
NDC: 0409-1181-30
Generic Equivalent: Meperidine HCl
Strength: 50 mg/ml
Delivery Method: Multiple Dose Vial
Drug Class: Synthetic, Opioids; Opioid Analgesics
Volume: 30 ml
Control: Class II
Buy Demerol online uk
What is Meperidine and How does it Work?
Buy Demerol online uk, Meperidine is used to help relieve moderate to severe pain. It may also be used before and during surgery or other procedures. Meperidine belongs to a class of drugs known as opioid (narcotic) analgesics and is similar to morphine. It works in the brain to change how your body feels and responds to pain![]()
Meperidine should not be used to treat long-term or ongoing pain. It should only be used to treat sudden episodes of moderate to severe pain. See also the Warnings and Precautions section.
Meperidine is available under the following different brand names:Buy Demerol online uk and pethidine.
Indications and Usage
- For the relief of moderate to severe pain
- For preoperative medication
- For support of anesthesia
- For obstetrical analgesia
Dosage and Administration
For Relief of Pain
Buy Demerol online uk, Dosage should be adjusted according to the severity of the pain and the response of the patient. While subcutaneous administration is suitable for occasional use, intramuscular administration is preferred when repeated doses are required. Buy Demerol online uk, If intravenous administration is required, the dosage should be decreased and the injection made very slowly, preferably utilizing a diluted solution. The dose of DEMEROL should be proportionately reduced (usually by 25 to 50 percent) when administered concomitantly with phenothiazines and many other tranquilizers since they potentiate the action of DEMEROL.
Adults. The usual dosage is 50 mg to 150 mg intramuscularly or subcutaneously every 3 or 4 hours as necessary. Elderly patients should usually be given meperidine at the lower end of the dose range and observed closely.
Children. The usual dosage is 0.5 mg/lb to 0.8 mg/lb intramuscularly or subcutaneously up to the adult dose, every 3 or 4 hours as necessary.
For Preoperative Medication
Adults. The usual dosage is 50 mg to 100 mg intramuscularly or subcutaneously, 30 to 90 minutes before the beginning of anesthesia. Elderly patients should usually be given meperidine at the lower end of the dose range and observed closely.
Children. The usual dosage is 0.5 mg/lb to 1 mg/lb intramuscularly or subcutaneously up to the adult dose, 30 to 90 minutes before the beginning of anesthesia.
For Support of Anesthesia
Repeated slow intravenous injections of fractional doses (e.g., 10 mg/mL) or continuous intravenous infusion of a more dilute solution (e.g., 1 mg/mL) should be used. The dose should be titrated to the needs of the patient and will depend on the premedication and type of anesthesia being employed, the characteristics of the particular patient, and the nature and duration of the operative procedure. Elderly patients should usually be given meperidine at the lower end of the dose range and observed closely.
For Obstetrical Analgesia
The usual dosage is 50 mg to 100 mg intramuscularly or subcutaneously when the pain becomes regular and may be repeated at 1- to 3-hour intervals.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate and discoloration before administration whenever solution and container permit.
How long does Demerol last
Overdosage
Symptoms. Serious overdosage with meperidine is characterized by respiratory depression (a decrease in respiratory rate and/or tidal volume, Cheyne-Stokes respiration, cyanosis), extreme somnolence progressing to stupor or coma, skeletal muscle flaccidity, Buy Demerol online uk, cold and clammy skin, and sometimes bradycardia and hypotension. In severe overdosage, particularly by the intravenous route, apnea, circulatory collapse, cardiac arrest, and death may occur.
Treatment. Primary attention should be given to the reestablishment of adequate respiratory exchange through provision of a patent airway and institution of assisted or controlled ventilation. The narcotic antagonist, naloxone hydrochloride, is a specific antidote against respiratory depression which may result from overdosage or unusual sensitivity to narcotics, including meperidine. Buy Demerol online uk, Therefore, an appropriate dose of this antagonist should be administered, preferably by the intravenous route, simultaneously with efforts at respiratory resuscitation.
An antagonist should not be administered in the absence of clinically significant respiratory or cardiovascular depression.
Oxygen, intravenous fluids, vasopressors, and other supportive measures should be employed as indicated.
NOTE: In an individual physically dependent on narcotics, the administration of the usual dose of a narcotic antagonist will precipitate an acute withdrawal syndrome. The severity of this syndrome will depend on the degree of physical dependence and the dose of the antagonist administered. The use of narcotic antagonists in such individuals should be avoided if possible. If a narcotic antagonist must be used to treat serious respiratory depression in the physically dependent patient, the antagonist should be administered with extreme care and only one-fifth to one-tenth the usual initial dose administered.
| Quantity | 50 Pills, 100 Pills, 200 Pills |
|---|
Be the first to review “Demerol 50mg/ml 30ml ampul” Cancel reply
Related products
Pain Relievers
Pain Relievers
Pain Relievers
Pain Relievers
Pain Relievers
Pain Relievers
Pain Relievers
Pain Relievers









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.